You’ve probably eaten several General Mills products within the last few weeks. In a General Mills SWOT analysis, we introduce you to this well-known food company with a wide range of consumer food items that have won a lot of fans. General Mills has won over consumers’ hearts and taste buds with its wide range of products, from well-known names like Cheerios and Betty Crocker to fan favorites like Yoplait and Haagen-Dazs. This SWOT analysis looks at General Mills’ strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats in the food business against their fierce competitors.
Table of Contents
General Mills History
General Mills Inc., one of the top manufacturers of packaged consumer foods, sells its goods in more than 100 nations. The corporation was established in 1928 to acquire the 1866-established Washburn Crosby Corporation, a flour milling business, as well as several lesser milling firms. Golden Valley, Minnesota, serves as its administrative center.
General Mills introduced several of its most well-known trademarks and goods in the ensuing decades, including Betty Crocker cake mixes in 1947 and Cheerios (formerly known as CheeriOats) in 1941. The corporation expanded into several industries, including electronics, apparel, and toys, but by the late 20th century, it had refocused on the food sector.
In an analysis, it has used branding, advertising, and product placement in marketing food items in a way that few other businesses at the time did. They have been able to keep a strong presence in the market because of this tactic.
Over the years, the corporation has acquired several noteworthy businesses. It eventually acquired the Red Lobster and Olive Garden restaurant brands, which had previously split off into Darden Restaurants in 1995 and the Pillsbury Company in the 1970s, respectively.
The main tenets of General Mills’ strategy for competing have been innovation, diversity, and acquisition. General Mills has maintained a varied portfolio, stayed competitive in the market, and kept up with shifting customer tastes and trends by launching new goods and brands, expanding into new areas, and buying other businesses.
In response to the growing consumer demand for healthier, more environmentally friendly food options, General Mills has also recently emphasized sustainability and health. The business aims to increase the nutritional value of its goods, lessen its impact on the environment, and source its materials more sustainably.
In February 2023, in a General Mills SWOT analysis, the ‘Accelerate’ strategy was focused on prioritizing resources to drive shareholder returns. Two businesses are key contributors to General Mills. North American retail and Pet food are two areas where General Mills is thriving. North America Retail has grown or maintained its share in the majority of its priority businesses in the past five fiscal years.
Pet Food has grown its distribution in the U.S. by four times and more than doubled its household penetration since the company entered the category. To learn more about the ‘Accelerate’ strategy, look at General Mills’ strengths below.
General Mills At-A-Glance
| Company | General Mills |
| Industry | Food Manufacturing |
| Founder | James Ford Bell |
| Year founded | 1928 |
| CEO | Jeff Harmening |
| Headquarters | Minneapolis, Minnesota |
| Number of employees | 35,000+ (2020) |
| Revenue (FY 2020) | US $17.63 Billion (2020) |
General Mills SWOT Analysis:
A SWOT analysis is a framework used to assess a company’s competitive situation and to create strategic planning. By taking General Mills’ strengths and weaknesses, as well as General Mills’ threats and opportunities, into account, we may better gain in-depth knowledge about General Mills. In this article, we’ll be taking a look at General Mills’ SWOT framework to better understand its competitive position and potential for future growth. See how General Mills competitors fare against them and learn about General Mills’ strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
General Mills Strengths:
The areas where a company excels above average or in a manner that distinguishes it from its rivals are its strengths. General Mills’ strengths are outlined in this General Mills SWOT analysis, which will highlight its strengths compared to Genera Mills competitors, including:
General Mills has used a variety of tactics to stay one step ahead of its rivals, including:
Accelerated Strategy: This plan of action is focused on allocating the company’s resources in a way that will maximize shareholder profits. It involves choices regarding where to concentrate efforts and how to gain competitive advantages. The generation of long-term shareholder value is anticipated to result from this strategy.
Boosted Competitiveness: General Mills has boosted its competitiveness by putting more emphasis on brand creation, more pertinent innovation, and more investments in growth projects. Consistently competing effectively. In the past five years, the company has been able to increase or maintain its market share in the majority of its priority businesses by investing more in brand development, innovation, and superior sales and supply chain execution in the North American retail segment.
Focus on pet food: Since General Mills joined the market through an acquisition in 2018, the company’s fastest-growing worldwide platform has experienced considerable growth. The Blue Buffalo brand is a pioneer in the humanization of pet food and care, and the business intends to keep growing by adding additional product lines and entering foreign markets.
Brand Equity: General Mills is the owner of a variety of well-known and respected brands, including Betty Crocker, Häagen-Dazs, and Cheerios. These brands have a significant following, which gives them a competitive edge.
Wide Product Range: General Mills offers a variety of items in several food categories. This product variety lessens reliance on a particular category and assists the business in reducing the risks associated with shifting consumer preferences.
What brands does General Mills own?
General Mills owns a diverse portfolio of well-known consumer food brands. While the ownership and composition of brand portfolios can change over time due to acquisitions, divestitures, or licensing agreements, here are some prominent brands that General Mills has owned or currently owns:
- Cheerios
- Wheaties
- Lucky Charms
- Trix
- Cinnamon Toast Crunch
- Nature Valley
- Fiber One
- Häagen-Dazs (under license from General Mills)
- Yoplait (in the United States and Canada)
- Pillsbury
- Betty Crocker
- Old El Paso amongst others
Global Presence: General Mills has operations in numerous nations. The organization can access a variety of markets and customer bases because of its global presence.
General Mills continually makes research and development investments in order to launch new goods and adapt to shifting consumer tastes. One of their primary strengths is their capacity for innovation and market trend adaptation.
Sustainable Business Practices: The company is firmly committed to sustainable and responsible business practices that not only benefit the environment but also appeal to customers who are becoming more and more ecologically aware.
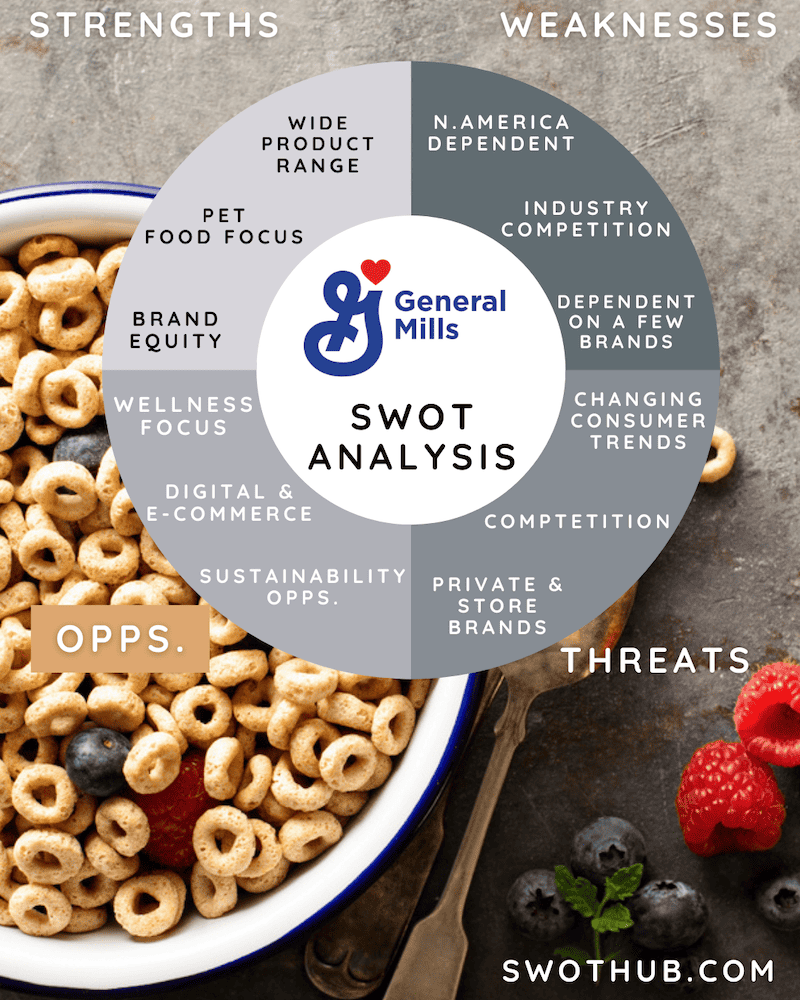
General Mills Weaknesses:
Weaknesses of a company are those that limit its potential, make it less competitive, and prevent it from achieving its goals. In this section, we’ll look at General Mills’ weaknesses.
Dependence on the North American Market: Despite General Mills’ presence on a global scale, most of its sales are generated in this region. If the North American market experiences economic downturns or other unfavorable circumstances, this high dependence could be a potential liability.
Industry competition: In a SWOT analysis, competition is fierce in the food and beverage sector. Many major international firms with comparable or even greater resources compete with General Mills.
Dependence on a small number of important brands: General Mills is very dependent on a small number of important brands, including Cheerios, Yoplait, and Nature Valley. Even though these brands hold dominant market positions, the company’s reliance on them leaves it vulnerable to dangers brought on by shifting customer tastes and heightened competition.
Failure to adequately adapt to changing market trends: The food sector is continually changing due to altering consumer demands. The rapid emergence of plant-based alternatives, healthier eating habits, and organic and natural food options could make it difficult for General Mills to quickly respond to these developments. Competitors with a competitive advantage may be more flexible and sensitive to these developments.
General Mills Opportunities:
General Mills has quite a few ways to get ahead of its competitors. We will examine some of General Mills’ opportunities compared to competitors including:
Strong brand portfolio: Cheerios, Betty Crocker, Yoplait, and Pillsbury are just a few of General Mills’ well-known and diverse brand names. General Mills has the chance to take advantage of its current consumer loyalty and broaden its product offerings within these well-known brands, thanks to this high brand equity. Under these brands, General Mills can roll out new variations, line extensions, or cutting-edge product innovations, relying on consumer familiarity and confidence.
Focus on health and wellbeing: General Mills has an opportunity to create and promote products that are consistent with consumer preferences due to the shift towards healthier eating habits and wellness. General Mills can spend money on R&D to develop healthier versions of its current products or launch brand-new product lines that address dietary requirements, such as gluten-free, organic, or plant-based options. General Mills may draw in health-conscious customers and set itself apart from rivals by providing healthier substitutes.
Expand into new markets: In a General Mills SWOT analysis it has a substantial position in the North American market, and there are chances for growth in other international regions as well. General Mills can expand into new geographical areas or solidify its current position in international markets by utilizing its experience and recognized brands. General Mills may take advantage of the rising demand for packaged food items in new regions by adapting its products and marketing techniques to local preferences, thereby expanding its worldwide market share.
Initiatives in digital and e-commerce: General Mills has the chance to improve its online presence and interact with customers directly as a result of the digital revolution and the growth of e-commerce. General Mills can reach a larger audience, increase brand awareness, and gain insightful consumer data by investing in digital marketing, social media interaction, and e-commerce platforms. Additionally, direct-to-consumer initiatives can assist General Mills in forging stronger ties with its clients and gathering information for focused marketing campaigns. Examples include subscription services or customized product offerings.
Sustainability and corporate responsibility: Customers are increasingly looking for brands that share their values, such as corporate responsibility and environmental sustainability. General Mills has the chance to improve its sustainability programs, which include waste reduction, ethical sourcing, and support for neighborhood initiatives. General Mills can strengthen its brand image, entice environmentally sensitive customers, and set itself apart from rivals by showcasing its dedication to sustainable practices.
General Mills Threats:
Threats pose a risk to every company’s stability and profitability. In this General Mills SWOT analysis, we will address some of the threats that are important to examine.
In a SWOT analysis of General Mills, some of its largest threats compared to competitors include:
Fierce Competition: General Mills competes in a market that is dominated by both large, well-established food corporations and fast-growing startups. Competitors could release comparable goods, copy profitable business models, or provide more affordable options. The market share of General Mills may decline as a result of the competition, which will also make it harder for it to charge premium prices.
General Mills’ largest competitors:
- Kelloggs Company: Known for their cereal brands like Corn Flakes and Frosted Flakes, Kellogg also makes snacks, cookies, crackers, and more.
- PepsiCo: While best known for its soft drinks, PepsiCo is also a major player in the food industry. The company owns Quaker Oats (which produces cereals and other grain products) and Frito-Lay (a leading snack brand).
- Nestlé: This Swiss multinational food and drink processing conglomerate is the largest food company in the world by revenue. It offers a wide range of products, including baby food, medical food, bottled water, breakfast cereals, coffee and tea, confectionery, dairy products, ice cream, frozen food, pet foods, and snacks.
- Kraft Heinz: Kraft Heinz is another big name in the food and beverage industry, known for its dairy products, snacks, beverages, cheese, and convenience foods.
- Mondelez International: This American multinational confectionery, food, holding, and beverage and snack food company is known for brands like Oreo, Cadbury, and Trident gum.
Changing Consumer Trends: In a General Mills SWOT analysis, trends and tastes are subject to quick change, notably in the food business. Consumer choice shifts in favor of healthier options, organic foods, and plant-based substitutes, which pose a danger to General Mills. General Mills runs the danger of losing market share to rivals who are more responsive to shifting consumer needs if it does not adjust and match these changing tastes.
Private label and store brands: General Mills is at risk from private label and store brands, which are frequently less expensive substitutes for branded goods. Retailers have been making investments in their private label products’ quality and marketing to win the trust and loyalty of their customers. To preserve price premiums and shelf space for its own branded products, General Mills may run into difficulties if private label companies significantly increase their market share.
Private labeling and store brands: In a General Mills SWOT analysis in terms of product labeling, ingredient transparency, and food safety requirements, the food business is subject to stringent restrictions and growing public scrutiny. Reputational harm, legal repercussions, or product recalls can result from failing to follow regulations or handle food safety issues. To lessen these risks and preserve customer confidence, General Mills must continue to be on guard and make quality control investments.
General Mills Competitors:
General Mills, and its competitors would fall under the “threats” category. Here are some of General Mills’ main competitors in the manufactured goods industry.
SWOT Analysis for General Mills: Conclusion and Recommendations:
General Mills needs to focus on several key strategies to remain competitive in the food industry.
Promote innovation: In a General Mills SWOT analysis, it needs to promote innovation and create new goods that are in line with shifting consumer expectations. General Mills should keep investing in research and development. This includes creating healthier options, investigating plant-based substitutes, and addressing certain dietary requirements.
Strengthen global expansion: General Mills should concentrate on increasing its presence in global markets, particularly in regions that are experiencing significant growth. This can be accomplished through strategic alliances, purchases, or regionally specific market entry initiatives. General Mills may lessen its reliance on established markets and access fresh opportunities for growth by expanding its worldwide reach.
Embrace digital transformation: To improve its online presence and get in front of more customers, General Mills should embrace digital technologies and make use of e-commerce channels. General Mills can increase consumer engagement, obtain insightful data, and more effectively target its marketing efforts by investing in digital marketing, data analytics, and tailored customer experiences. A company can improve efficiency and customer satisfaction by improving its supply chain and distribution networks to satisfy e-commerce demands.
Boost sustainability programs: General Mills should keep placing a high priority on corporate responsibility and sustainability. General Mills SWOT analysis, it can set itself apart from rivals and satisfy rising consumer demand for ethical and sustainable practices by making investments in sustainable sourcing, minimizing environmental impact, and supporting social activities. Transparently informing consumers of these initiatives can
FAQs for General Mills
What are General Mills’ weaknesses?
General Mills faces challenges like heavy dependence on traditional processed foods, which are falling out of favor, and intense competition in the food industry. Additionally, fluctuating commodity prices impact its cost structure, affecting profitability.
What is General Mills’ competitive advantage?
General Mills’ competitive advantage lies in its strong brand portfolio, including well-known names like Cheerios and Häagen-Dazs. Its extensive distribution network and strategic marketing efforts further enhance its market position.
How can General Mills continue to stay competitive?
To stay competitive, General Mills can focus on product innovation, catering to health-conscious consumers, and expanding its presence in emerging markets. Investing in sustainable practices and digital transformation can also drive long-term competitiveness and appeal to modern consumers.
These suggestions are meant to give General Mills a strategic course that will help it successfully navigate the market. However, General Mills must evaluate and rank these suggestions in light of its business objectives, available resources, and market circumstances.