Toyota advantages set them above their competitors in the automotive industry. It thrives on heavy-hitter competitors such as Honda, Ford, and Toyota. This Toyota SWOT analysis will highlight Toyota’s advantages and also show how this iconic car brand was one of the first pioneers of the industry and its strengths and weaknesses.
Table of Contents
Toyota History
One of the largest automotive corporations in the world and the largest Japanese automaker is Toyota Motor Corp. The Toyota Motor Co., Ltd. was incorporated in 1937 after being founded in 1933 as a section of the Toyoda Automatic Loom Works, Ltd. Toyota later founded a number of similar businesses, such as Toyota Auto Body, Ltd. and Toyoda Machine Works, Ltd. (1945).
The business quickly grew during the 1960s and 1970s, selling lots of cars to other countries. After many of its business segments were consolidated, the corporation adopted the name Toyota Motor Corp. in 1982. It owns businesses that manufacture automobiles and automobile parts, trucks, steel, synthetic resins, and industrial equipment.
Toyota and Lexus are two of its brands. In the car manufacturing sector, Toyota Motor Corporation is a significant player. Lexus and BMW are longtime competitors. The industry is in a better position than it was five years ago and has grown by 4.5% to generate $3 trillion in revenue since then. Toyota is currently the world’s most powerful auto manufacturing company and has a significant distribution footprint in several developed nations.
The question here arises is why Toyota is the best and has gained a competitive advantage over other car manufacturers for many years, so the answer is Toyota’s production system. Toyota developed the Toyota Production System (TPS), a business model that focuses on streamlining processes and fostering a culture of continuous improvement.
It is set up as a collection of resources that Toyota uses across the board. Everything is under its control, including the development of new products and their production, business logistics, and interactions between the company and its suppliers and customers. So that’s why we can say that Toyota is the best among all other car manufacturers.
Toyota SWOT Analysis – At a Glance
| Name | Toyota Motor Corporation |
| Website | Toyota |
| Founded | August 28, 1937 |
| Founder | Kiichiro Toyoda |
| Industries served | Automotive, Housing, Financial Services, Other |
| Geographic areas served | Worldwide (over 170 countries) |
| Headquarters | Toyota, Aichi, Japan |
| Current CEO | Akio Toyoda |
| Revenue (JP¥) (US$) | 27.2 trillion (2021) 245 billion (2021) |
| Profit (JP¥) (US$) | 3 trillion (2021) 23 billion (2021) |
| Employees | 366,300 (2021) |
Toyota Advantages – History of this Powerful Car Company
Toyota SWOT Analysis
Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats are referred to as SWOT. Strategic planning frequently uses a technique called SWOT analysis, which was developed at Stanford in the 1970s. In this article, we’ll be taking a look at Toyota SWOT analysis & top Toyota advantages and disadvantages to better understand its competitive position and potential for future growth. Read on to learn more about their Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats.
Toyota Advantages
Toyota’s advantages: Toyota’s advantages over other brands of cars include quality, durability, safety, affordability, environmental leadership, fun-to-drive abilities, and fashionable design.
Toyota disadvantages: Some of the disadvantages of Toyota company cars over car brands include forced acceleration, faulty air conditioning, faulty water pumps, common fuel pump failures, oil sludge in engines, and brake and suspension issues.
Toyota SWOT Analysis Strengths
A company’s strengths are those things that it performs exceptionally well or in a way that sets it apart from its competitors. The SWOT analysis of Toyota company outlines Toyota’s advantages and top strengths. Some of the strengths are discussed below:
Global presence: Around the world, Toyota has retail locations, subsidiary businesses, and production facilities. Toyota automobiles are sold in more than 170 nations across numerous continents, accounting for 10.5% of the world market, from Asia to Europe, Africa, and America.
Quality, Durability, Reliability: The core values of Toyota are unwavering and cutting-edge standards of Quality, Durability, and Reliability (QDR). Toyota makes a $1 million investment in worldwide R&D per hour. Every Toyota is designed to be a car that will never break down.
Diversified vehicle range: Toyota provides a wide range of automobiles, including the Corolla, Prius, Camry, Land Cruiser, Scion, Hilux, Supra, and many others. The vehicles come in a variety of styles, including sedans, pickup trucks, and off-roaders. They can be driven by an electric, hybrid, gasoline, or diesel engine, which enables the business to serve customers in the whole vehicle market.
Effective Leadership: Toyota has avoided the conflict and unrest seen in other auto firms like Nissan because of its excellent organizational structure and leadership. The organization’s stability has been improved via structure and leadership.
Exceptional car value: Toyota produces cars with enjoyable ownership experiences. Even after many years, ownership, operation, and resale are all satisfying. Toyota owners receive outstanding value in addition to quality automobiles.
Safety focus; A sense of “Waku Doki,” a Japanese term that means “the extreme adrenaline rush,” is created by Toyota’s strong emphasis on safety, which on the one hand keeps you at ease and, on the other, gets your pulse racing with a range of fascinating cars.
Toyota SWOT Analysis Weaknesses
Weaknesses are aspects that limit an organization’s potential, reduce its capacity to compete, and hinder it from achieving its goals. In this section of Toyoya SWOT analysis; we will analyze some of the weaknesses or disadvantages of Toyota after discussing its strengths.
Ineffective marketing: Although Toyota uses cutting-edge green vehicle technology to produce eco-friendly cars, the business has been unable to effectively promote and gain market share for these in-demand innovations.
Organizational culture of secrecy: Toyota’s global hierarchical organizational structure limits regional operations’ ability to be as flexible as possible. Additionally, the company’s culture of secrecy is a flaw that slows response times in dealing with new issues.
Faulty fuel pumps: Toyota’s production and design aren’t perfect, despite the fact that it sets the bar for quality control. For instance, Toyota recalled 700,000 vehicles at the beginning of this year due to a defective fuel pump. Such circumstances diminish consumer faith in the brand and can destroy years of goodwill.
Low brand awareness: Hino, Lexus, Daihatsu, and Toyota all have distinct flagship models, but only Lexus and Toyota have been successful in building their brands.
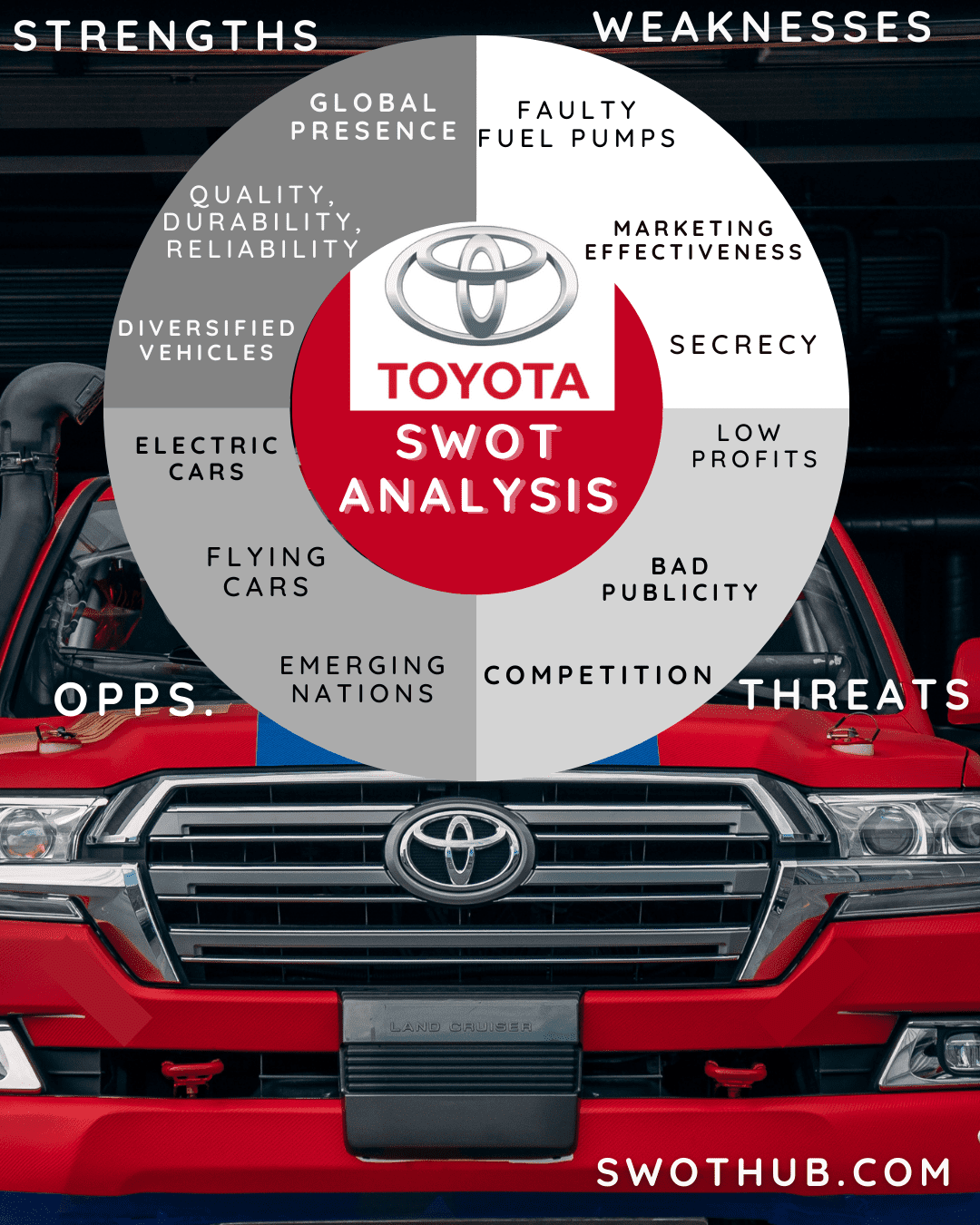
Toyota SWOT Analysis Opportunities
Toyota operates in a world filled with endless possibilities. These opportunities will continue to be advantageous to organizations. The next phase of the Toyota SWOT analysis will examine some of the opportunities for Toyota to grow and diversify its business.
Focus on electric cars: Over the past few years, more consumers have become environmentally conscious. Toyota may take advantage of this chance by expanding its investment in and concentrating on producing environmentally friendly automobiles like hybrid and electric cars. By 2030, Toyota plans to sell around 5.5 million electrified vehicles, according to internal targets.
Flying cars: The Japanese firm SkyDrive successfully carried out the first manned test flight of its flying car. One of the businesses supporting SkyDrive is Toyota. Toyota is certain that its investment in the company will pay off, despite the fact that SkyDrive faces numerous technological and legal obstacles.
More attention to emerging Nations: Over the past few decades, the financial condition in emerging nations has significantly improved. Toyota may raise its investment in developing nations like China and benefit from the rising middle class’s constant need for automobiles.
Invest in Complementary Sectors: Toyota has the knowledge and resources to work in various auto-related or connected industries, such as the production of motorcycles and multi-modal transportation services.
Toyota SWOT Analysis Threats
Threats put any company’s stability and profitability in danger. In this section of Toyota’s SWOT analysis, we’ll talk about some of the market risks that the business faces. Some of the threats to Toyota’s SWOT analysis are discussed below:
Low Profits: The threat of fluctuating currency rates is constant. When the money is returned back to Japan in the Yen, the profit is significantly lower than it would be in another currency.
Bad publicity: Consumers are frequently shown images of terrorist organizations, renegade soldiers, and armies of rogue governments riding Toyota off-road vehicles. The link with terror, violence, and conflict zones can have an impact on sales, even though it is a testimonial to the product’s performance in all environments.
New entrants: Due to the high capital needs in the automotive industry, the threat of new entrants is limited. Large companies, like those from China, for example, pose a serious danger to the company. Chinese businesses might enter markets where Toyota is already present and start selling their goods there.
Intense Competition: Ridesharing services, old rivals like Nissan, Ford, Volkswagen, BMW, Mitsubishi, and Hyundai, as well as several newcomers, are increasing the competition for Toyota on the global market. There is slower growth in profitability and market share as a result of rising Toyota competition.
Strongest Toyota Competitors
Toyota’s top direct competitors are:
- Ford
- Volkswagen
- Hyundai
- General Motors
- Nissan
- BMW (Lexus brand competitor)
These companies employ 1 million people worldwide, with Toyota employing only 359 thousand people and ranking first among Toyota’s Top 5 competitors. The top five competitors employ an average of 211 thousand people.
Toyota faces competition from low-cost automobiles made by Korean, Chinese, and Indian manufacturers, who have been expanding their presence in foreign markets. Toyota also faces the threat of competitors’ rapid innovation, such as GM, Honda, and Ford. Toyota’s advantages will be crucial to maintaining against their competitive edge with innovation and constantly staying one step ahead.
Toyota Conclusion: Accentuate Toyota Advantages!
Hence, it is concluded from the above Toyota SWOT analysis that Toyota has a significant market share in the car manufacturing industry. Toyota has risen to the top of the car industry because of 90 years of relentless pursuit of perfection. Toyota, a pioneer in manufacturing, marketing, and research, is essential to bridging the transition from the era of fossil fuels to the era of clean energy. One of the major advantages of the Toyota Company is its environmentally friendly green car projects, such as electric and hybrid cars. The company’s weaknesses are based on its organizational structure and culture, as well as the effects of competition. Some of the recommendations for the Toyota car manufacturing company are:
- The TPS Toyota manufacturing system, which is widely recognized, must be followed first. In this arrangement, the production quality of the cars is given more weight.
- As the market grows, it will take into account the number of customers rather than the number of automobiles sold.
- Toyota must leverage its competitive advantage based on its inventive skills and environmentally friendly automobile projects to counter the dangers posed by the competition.
- The organization might further modify its culture and organizational design to enhance its capacity for flexibility in making decisions and solving problems.
FAQs SWOT Analysis of Toyota Motor Corporation
Which external threats should Toyota prioritize and why?
Toyota should prioritize threats like intense competition, disruptive technologies, and changing consumer preferences to maintain market leadership and adapt to evolving industry trends.
What competitive advantage does Toyota have?
Toyota’s competitive advantage stems from its renowned quality, efficient manufacturing processes (e.g., Toyota Production System), and a strong global supply chain.
What companies did Toyota make?
Toyota has subsidiaries like Lexus and Scion, and it collaborates with other companies, but it’s distinct from them. These subsidiaries offer different vehicle lines under the Toyota umbrella, catering to various markets and consumer preferences.